SMS Analytical has an ever growing range of techniques and including various aspects of chromatography, spectroscopy as well as classic chemistry methods.
SAMPLE PREPARATION
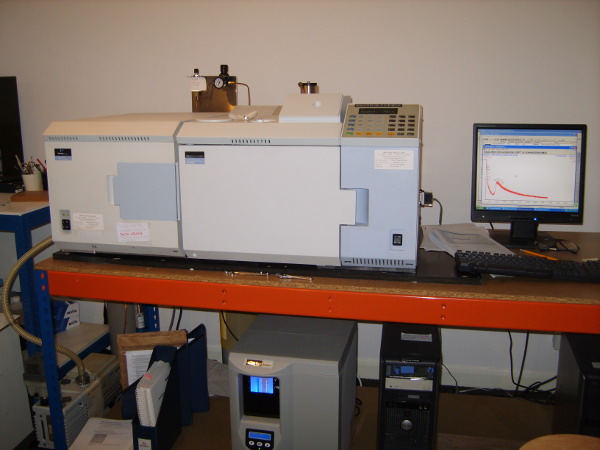
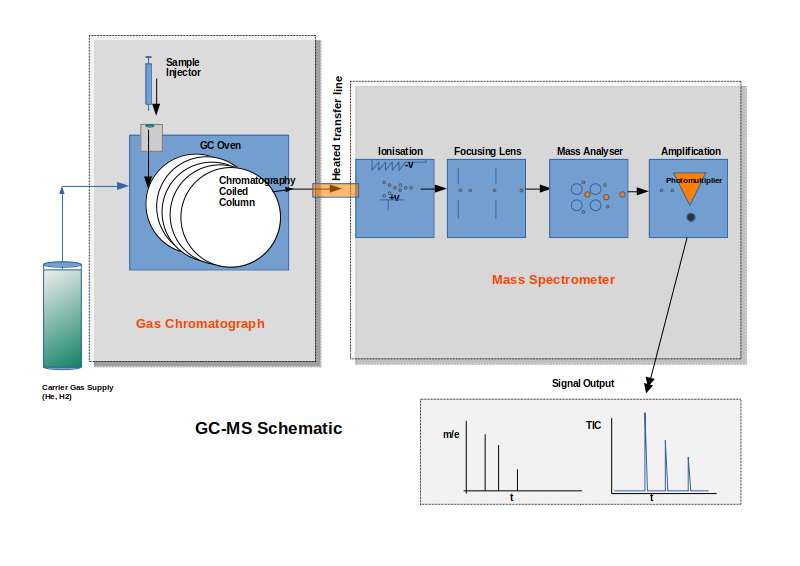
GC-MS
There are many examples of GC-MS use including the following:
- Fire debris analysis – looking for accelerant traces using head-space vapour sampling
- Determining the presence of ‘Smoke Taint’ compounds in foodstuffs such as vegetables.
- Oil pollution analysis: CEN15522:2 2006
- Nordtest methods
Also, the identification of trace components / contaminants in
- Packaging
- Polymeric foams
- Coolant system fluids
We have two GC-MS systems, one of which includes an auto-sampler providing 24/7 analysis when needed.
HPLC
 This is our first high performance liquid chromatography system (HPLC). It is currently using a UV detector and has a ternary gradient capability as well as a column oven thus providing high level of customised chromatographic conditions.
This is our first high performance liquid chromatography system (HPLC). It is currently using a UV detector and has a ternary gradient capability as well as a column oven thus providing high level of customised chromatographic conditions.
The HPLC allow SMS to provide additional methods include dyes in diesel fuels, Poly Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAH) in foods and can be further expanded with alternative detector modules (Fluorescence, Conductivity, etc. ) in the future.
TLC
UV-Vis SPECTROMETRY
INFRARED SPECTROMETRY
Examination of a wide range of organic materials including polymer foams. Use of a new sensitive diamond ATR for very small sample quantities.
TITRIMETRY
COLOURIMETRIC METHODS
Sulphate (BaCl2) and Silicate.
MICROSCOPY
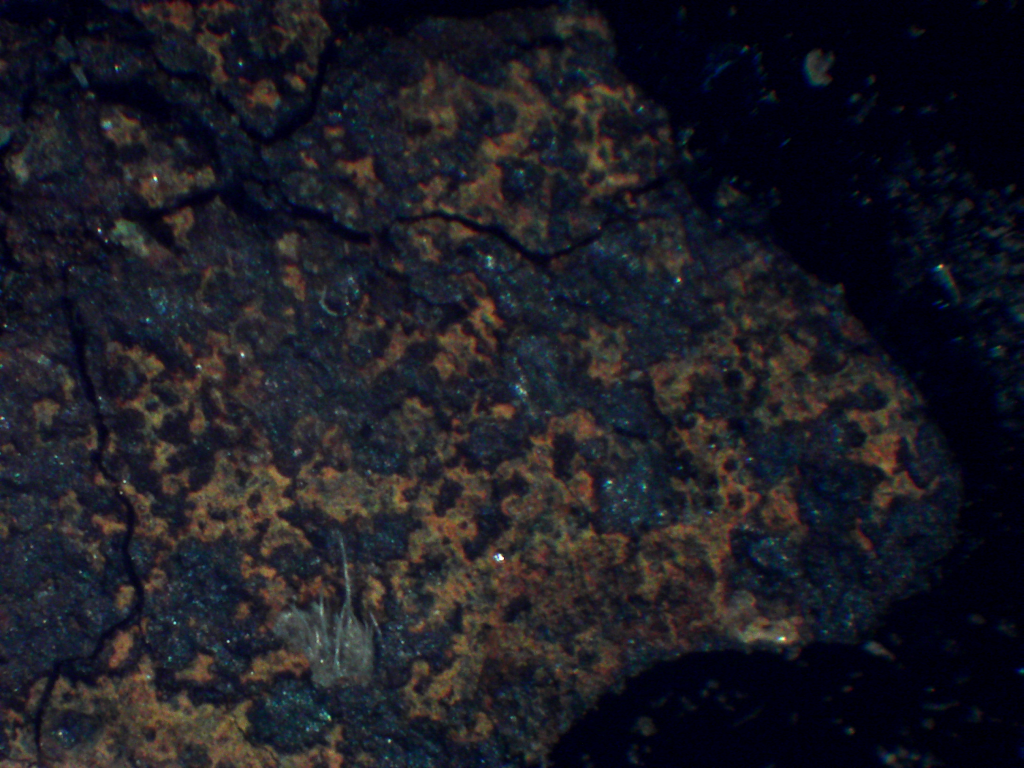
Optical Microscopy
We have our own microscope with a camera attachment so can characterise the morphology of samples. The following is a rust sample:
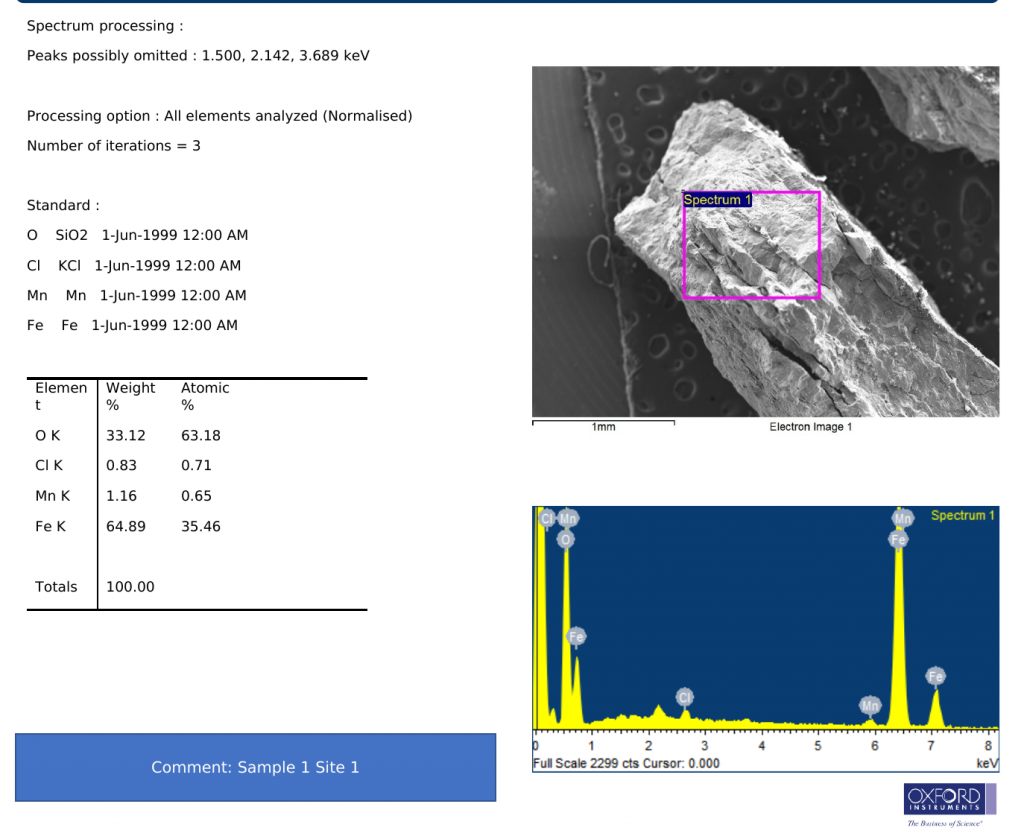
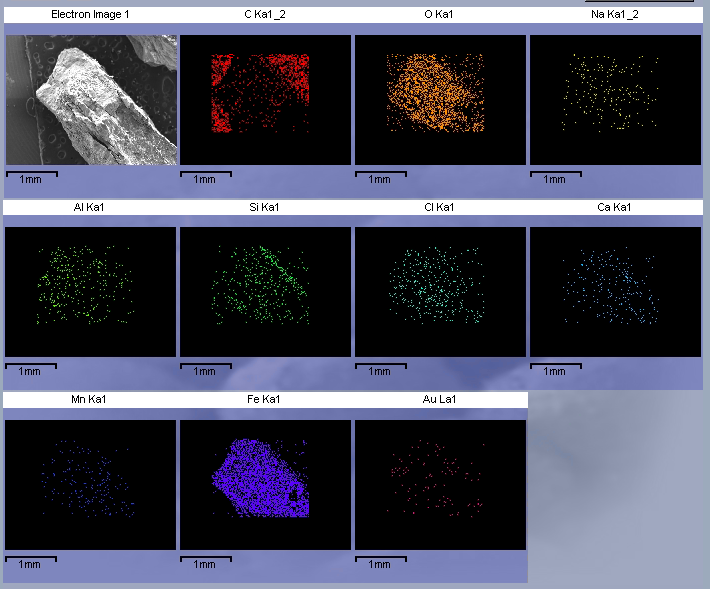
Scanning Electron Microscopy With Energy Dispersive X-Ray (SEM)
We use Scanning Electron Microscopy with Energy Dispersive X-Ray to give approximate elemental composition. Apart from sample morphology we also use this to obtain an approximate elemental composition (like XRF, the caveat here is that this is dependent on the matrix and surface flatness).